二叉树
约 1485 个字 240 行代码 5 张图片 预计阅读时间 8 分钟 总阅读量 次
101 对称二叉树
二叉树|迭代 + 递归
🔑🔑 难度:Easy 简单
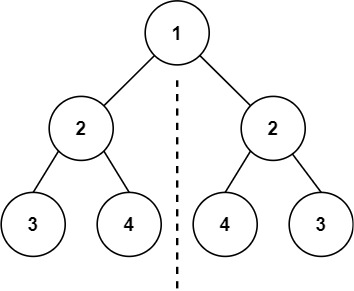
示例1: 给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
queue = deque()
queue.append(root)
while queue:
length = len(queue)
cur_num = []
for i in range(length):
cur = queue.popleft()
if cur.left:
queue.append(cur.left)
cur_num.append(cur.left.val)
else:
cur_num.append(-101)
if cur.right:
queue.append(cur.right)
cur_num.append(cur.right.val)
else:
cur_num.append(-101)
# print(cur_num)
if cur_num != list(reversed(cur_num)):
return False
return True
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
def check(p, q):
if p == None and q == None:
return True
if p == None or q == None:
return False
return p.val == q.val and check(p.left, q.right) and check(p.right, q.left)
return check(root.left, root.right)
迭代的做法,每一层看看是否对称,需要一个队列;
递归的做法,:它们的两个根结点具有相同的值,每个树的右子树都与另一个树的左子树镜像对称
我们可以实现这样一个递归函数,通过「同步移动」两个指针的方法来遍历这棵树,\(p\) 指针和 \(q\) 指针一开始都指向这棵树的根,随后 \(p\) 右移时,\(q\) 左移,\(p\) 左移时,\(q\) 右移。每次检查当前 \(p\) 和 \(q\) 节点的值是否相等,如果相等再判断左右子树是否对称。
437. 路径总和 III
定义子函数
🔑🔑 难度:Medium 中等
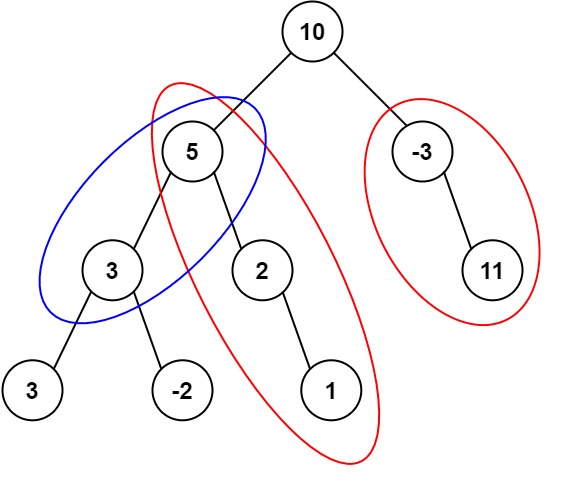
示例1: 给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 targetSum ,求该二叉树里节点值之和等于 targetSum 的 路径 的数目。
路径 不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
输入:root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8 输出:3 解释:和等于 8 的路径有 3 条,如图所示。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> int:
def rootSum(root, target):
if root == None:
return 0
cnt = 0
if root.val == target:
cnt += 1
cnt += rootSum(root.left, target - root.val)
cnt += rootSum(root.right, target - root.val)
return cnt
if root is None:
return 0
rv = rootSum(root, targetSum)
riv = self.pathSum(root.right, targetSum)
lev = self.pathSum(root.left, targetSum)
return rv + riv + lev
注意,最终结果的来源具体有:包含root,同时从root向右;包含root,同时从root向左;不包含root,此时就是递归了,分别检查左右各有几个。所以有一个函数要单独实现:包含root的路径搜寻。(对应上面的rootSum函数)
124. 二叉树的最大路径和
🔑🔑 难度:High 困难
二叉树中的 路径 被定义为一条节点序列,序列中每对相邻节点之间都存在一条边。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其 最大路径和 。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.maxValue = float('-inf')
def dfs(head):
if not head:
return 0
max_l = max(0, dfs(head.left))
max_r = max(0, dfs(head.right))
self.maxValue = max(self.maxValue, max_l + max_r + head.val)
return max(max_l, max_r) + head.val
dfs(root)
return self.maxValue
dfs(head) 返回的结果是“包含head的路径的最大值,因此,由两部分组成:左边的最大,右边的最大,加上自己。而每次递归的时候,都去判断一下,是否可以更新当前的value。而正因为是包含head的路径的最大值,所以这个函数本身返回的值,必须包括自己,剩下的,捡左右两边最大的(没有的话就都不选)。
105. 从先序和中序遍历构造二叉树
十分经典的递归:截断位置。
🔑🔑 难度:Medium 中等
示例1: 给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if len(inorder) == 0:
return None
cut = 0
for i in range(len(inorder)):
if inorder[i] == preorder[0]:
cut = i
root = TreeNode(preorder[0])
root.left = self.buildTree(preorder[1: cut + 1], inorder[:cut])
root.right = self.buildTree(preorder[cut + 1: ], inorder[cut + 1: ])
return root
226. 翻转二叉树
🔑🔑 难度:Easy 简单
示例1:
输入:
root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]输出:
[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root == None:
return None
right = self.invertTree(root.right)
left = self.invertTree(root.left)
root.left = right
root.right = left
return root
🌟208. 实现前缀树
🔑🔑 难度:Medium 中等
Trie(发音类似 "try")或者说 前缀树 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。这一数据结构有相当多的应用情景,例如自动补全和拼写检查。
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie()初始化前缀树对象。void insert(String word)向前缀树中插入字符串word。boolean search(String word)如果字符串word在前缀树中,返回true(即,在检索之前已经插入);否则,返回false。boolean startsWith(String prefix)如果之前已经插入的字符串word的前缀之一为prefix,返回true;否则,返回false。
示例:
输入
"Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"][], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]]输出null, null, true, false, true, null, true]解释 rie trie = new Trie(); rie.insert("apple"); rie.search("apple"); // 返回 True rie.search("app"); // 返回 False rie.startsWith("app"); // 返回 True rie.insert("app"); rie.search("app"); // 返回 True
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.children = [None] * 26
self.isEnd = False
def insert(self, word: str) -> None:
node = self
for ch in word:
ch_ = ord(ch) - ord('a')
if not node.children[ch_]:
node.children[ch_] = Trie()
node = node.children[ch_]
node.isEnd = True
def searchPrefix(self, prefix):
node = self
for ch in prefix:
ch_ = ord(ch) - ord('a')
if node.children[ch_] == None:
return None
node = node.children[ch_]
return node
def search(self, word: str) -> bool:
node = self.searchPrefix(word)
return node is not None and node.isEnd
def startsWith(self, prefix: str) -> bool:
return self.searchPrefix(prefix) is not None
# Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = Trie()
# obj.insert(word)
# param_2 = obj.search(word)
# param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix)
这里注意,我们的每个children 都是一个Trie类,构成一个大树。还需要注意,由于需要查找特定结尾的字符串是否在这个树中,所以需要添加 isEnd 属性,不然插入 'apple',会发现 'app' 这个词也能查找到,但是实际上这只是一个前缀;第三,注意我们自己实现了 searchPrefix 这个方法用来查找前缀。
543. 二叉树的直径
🔑🔑 难度:Medium 中等
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:3
解释:3 ,取路径 [4,2,1,3] 或 [5,2,1,3] 的长度。

# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.maxVal = 0
def dfs(head):
if not head:
return -1
L = dfs(head.left) + 1
R = dfs(head.right) + 1
self.maxVal = max(self.maxVal, L + R )
return max(L, R)
dfs(root)
return self.maxVal
可以记模板:到当前节点为止,其直径是其左侧的链条长 + 右侧的链条长,左侧链条如果为None,则需要返回0,而以该节点为孩子的父节点,其长度为该节点左右最长链条里选择一个。
230. 二叉搜索树中的第K小元素
🔑🔑 难度:Medium 中等
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,请你设计一个算法查找其中第 k 小的元素(从 1 开始计数)。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
self.K = k
self.result = 0
def dfs(head):
if not head:
return
if self.K == 0:
return
dfs(head.left)
self.K -= 1
if self.K == 0:
self.result = head.val
return
dfs(head.right)
dfs(root)
return self.result
模板题:二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是一个排序的数组,所以直接中序遍历,但是记录当前是“倒数第几个”,直到某次减为0
114. 二叉树展开为链表
🔑🔑 难度:Medium 中等
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
展开后的单链表应该同样使用 TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def flatten(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
"""
result = []
def preorder(head):
if not head:
return
result.append(head)
preorder(head.left)
preorder(head.right)
preorder(root)
for idx, node in enumerate(result):
if idx == len(result) - 1:
node.left = None
node.right = None
else:
node.left = None
node.right = result[idx + 1]
先过一遍先序遍历,然后根据这个顺序,重新连接二叉树的节点。